Professional Layer Pullet Cages for Poultry Development
Introduction to Layer Pullet Cages
The poultry industry has undergone significant transformations over the past decades, with technological advancements playing a crucial role in improving efficiency, animal welfare, and productivity. Among these advancements, professional layer pullet cages have emerged as essential equipment for modern poultry development. These specialized cages are designed to accommodate pullets (young hens) during their growing phase before they transition to egg-laying production systems.
Layer pullet cages represent a critical intermediate stage in poultry farming, bridging the gap between brooding and the laying period. Proper housing during this developmental phase directly impacts the future laying performance, health, and longevity of the birds. Modern pullet cage systems are engineered to provide optimal conditions for growth while maximizing space utilization and facilitating efficient management practices.
This comprehensive guide explores the design features, benefits, management considerations, and technological innovations associated with professional layer pullet cages, providing poultry farmers and industry professionals with valuable insights into this crucial aspect of poultry development.
Design Features of Professional Pullet Cages
Structural Components
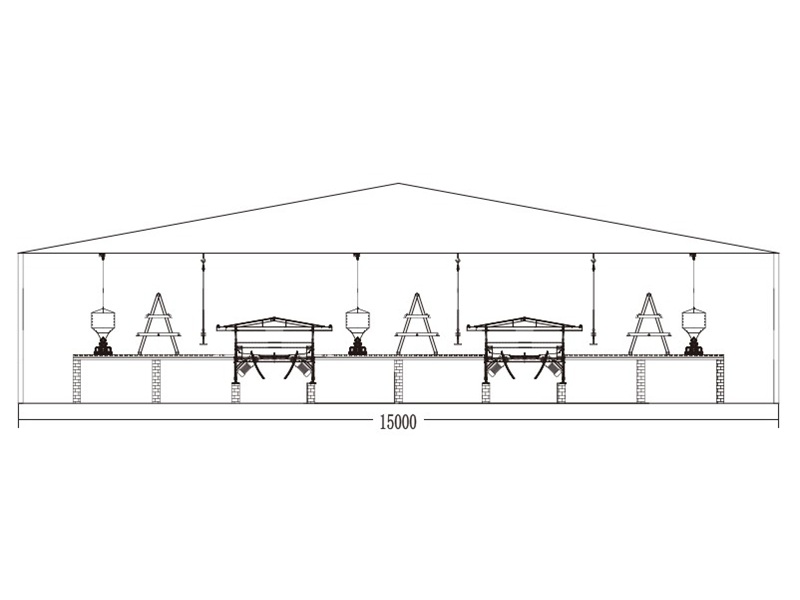
Professional layer pullet cages are constructed with durability and functionality in mind. The frame typically consists of galvanized steel, providing resistance to corrosion from moisture and ammonia in poultry house environments. The cage floors are made of welded wire mesh with appropriate spacing to support the birds comfortably while allowing manure to pass through.
The design incorporates:
- Multiple tiers (usually 3-5 levels) to maximize vertical space utilization
- Sloping floors to facilitate egg collection in systems where pullets begin early laying
- Integrated feed troughs and water lines positioned for easy access
- Manure collection systems beneath each tier
- Proper ventilation spacing between cages
Size and Space Requirements
Pullet cages are dimensioned according to the birds' growth stages:
- Starter cages (0-6 weeks): Smaller compartments with higher bird density
- Grower cages (6-16 weeks): Larger spaces accommodating growing birds
- Transition cages (16-18 weeks): Preparing pullets for layer cage systems
Space allocation follows industry standards of 200-300 cm² per bird, varying with breed and management system. The height of cages allows pullets to stand comfortably without touching the roof, typically 35-45 cm.
Specialized Features
Modern pullet cages incorporate several specialized features:
- Adjustable partitions: Allow for compartment size modification as birds grow
- Removable dividers: Facilitate vaccination and health checks
- Anti-cannibalism devices: Reduce pecking injuries
- Perches: Encourage natural roosting behavior
- Lighting systems: Integrated or compatible with house lighting programs
Benefits of Using Professional Pullet Cages
Improved Growth Performance
Pullet cages provide controlled environments that promote uniform growth:
- Consistent access to feed and water
- Reduced competition among birds
- Better monitoring of individual bird development
- Lower stress levels compared to floor systems
- Reduced incidence of diseases transmitted through litter
Enhanced Biosecurity
Cage systems offer significant biosecurity advantages:
- Physical separation from manure reduces pathogen exposure
- Easier to implement vaccination and medication programs
- Reduced contact with wild birds and rodents
- Simplified cleaning and disinfection between flocks
- Better control of parasitic infections
Operational Efficiency
Professional pullet cages streamline poultry management:
- Reduced labor requirements for daily operations
- Automated systems for feeding, watering, and climate control
- Efficient use of poultry house space
- Easier monitoring of feed consumption and growth rates
- Simplified bird handling during transfers
Animal Welfare Considerations
Modern pullet cage designs incorporate welfare features:
- Adequate space for natural behaviors like stretching and wing-flapping
- Proper perch space for resting
- Reduced feather pecking and cannibalism
- Improved air quality compared to some floor systems
- Better temperature regulation
Management Practices for Pullet Cages
Stocking Density and Group Size
Optimal stocking density varies by age and breed:
- 0-4 weeks: 50-60 birds/m²
- 4-8 weeks: 25-30 birds/m²
- 8-16 weeks: 15-20 birds/m²
- 16-18 weeks: 10-12 birds/m²
Group sizes typically range from 10-30 birds per cage compartment, allowing for social interaction while preventing overcrowding.
Feeding Programs
Pullet cage feeding requires special attention:
- Use of age-appropriate feed formulations (starter, grower, developer)
- Controlled feed distribution to ensure uniform access
- Adjustment of feeder space as birds grow (from 2.5 cm/bird to 7.5 cm/bird)
- Monitoring of feed conversion ratios
- Implementation of restricted feeding programs when necessary
Water Management
Water systems in pullet cages should provide:
- 1-2 cm of drinking space per bird
- Proper nipple or cup placement at bird height
- Regular cleaning and sanitization
- Monitoring of water consumption patterns
- Protection from contamination
Lighting Programs
Light management in pullet cages affects sexual maturity:
- Gradual reduction from 20-24 hours to 8-10 hours by 12 weeks
- Controlled intensity (5-10 lux initially, reduced to 2-5 lux)
- Use of dimmers for gradual changes
- Consistent photoperiods to prevent stress
- Preparation for layer house lighting conditions
Health Monitoring
Regular health checks in cage systems should include:
- Daily observation of bird behavior and activity
- Monitoring of feed and water consumption
- Weekly weight sampling (2% of population)
- Examination for signs of respiratory distress
- Checking for external parasites
- Assessment of manure quality
Transition from Pullet to Layer Cages
Preparation for Transfer
The transition process requires careful planning:
- Matching lighting programs between pullet and layer houses
- Acclimatization to new feed formulations
- Health assessment before movement
- Adjustment of cage space allowances
- Preparation of equipment in the layer house
Transfer Timing
Optimal transfer periods:
- Standard breeds: 16-18 weeks
- Early-maturing hybrids: 15-17 weeks
- Late-maturing breeds: 18-20 weeks
- Consideration of flock uniformity
- Avoidance of extreme weather conditions
Transfer Methods
Best practices for moving pullets:
- Use of specialized transfer equipment
- Minimizing handling stress
- Maintaining group integrity when possible
- Provision of immediate access to water
- Monitoring post-transfer behavior
Technological Advancements in Pullet Cage Systems
Automation Integration
Modern systems incorporate various automated features:
- Computer-controlled feeding systems
- Automated water quality monitoring
- Climate control systems linked to cage environments
- Weight monitoring through electronic scales
- Data collection for performance tracking
Environmental Control
Advanced environmental management includes:
- Precision ventilation systems
- Ammonia and humidity sensors
- Temperature zoning for different cage levels
- Air filtration options
- Heat recovery systems
Data Analytics
Emerging technologies enable:
- Growth curve monitoring
- Early detection of health issues
- Feed efficiency optimization
- Prediction of sexual maturity
- Integration with farm management software
Welfare Enhancements
Innovative welfare features:
- Environmental enrichment devices
- Dynamic space adjustment systems
- Behavioral monitoring cameras
- Stress reduction technologies
- Improved perch designs
Economic Considerations
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Factors to consider when investing in professional pullet cages:
- Initial investment vs. long-term savings
- Labor cost reductions
- Improved feed conversion ratios
- Reduced mortality rates
- Higher quality pullets for egg production
Return on Investment
Key performance indicators:
- Uniformity rates at transfer
- Age at first egg
- Peak production levels
- Persistency of lay
- Feed costs per dozen eggs
Maintenance Requirements
Ongoing costs include:
- Regular inspection and replacement of worn components
- Cleaning and disinfection between flocks
- Lubrication of moving parts
- Replacement of water system components
- Structural integrity checks
Future Trends in Pullet Cage Development
Sustainable Materials
Emerging trends in cage construction:
- Use of recycled materials
- Biodegradable components
- Improved corrosion-resistant coatings
- Lightweight yet durable alloys
- Modular designs for easier replacement
Smart Cage Technologies
Future developments may include:
- Individual bird identification systems
- Real-time health monitoring
- Automated adjustment of cage configurations
- Integration with artificial intelligence
- Predictive analytics for management decisions
Welfare-Focused Designs
Anticipated improvements:
- Enhanced behavioral expression opportunities
- Dynamic space allocation
- Improved social interaction designs
- Stress-reducing environmental controls
- Natural light simulation systems
Conclusion
Professional layer pullet cages represent a critical component in modern poultry production systems, offering numerous advantages in terms of bird health, growth performance, and operational efficiency. The careful design and proper management of these cage systems directly contribute to the development of high-quality laying hens capable of achieving their genetic potential.
As the poultry industry continues to evolve, pullet cage technology is keeping pace with advancements in automation, data analytics, and animal welfare considerations. The integration of smart technologies and sustainable practices promises to further enhance the effectiveness of these systems while addressing societal concerns about poultry production methods.
For poultry producers, investment in professional pullet cage systems represents a strategic decision that can yield significant returns through improved flock performance and reduced operational costs. By implementing best practices in cage management and staying informed about technological developments, poultry professionals can optimize their pullet development programs and establish a solid foundation for successful egg production operations.
The future of pullet cage systems lies in the balance between economic efficiency, technological innovation, and animal welfare—a challenge that the poultry industry continues to address through research, development, and practical experience in commercial operations worldwide.

 Catalogue
Catalogue







 ada apa
ada apa Telepon
Telepon
Komentar
(0)